How Green HRM Strengthens Organizational Sustainability
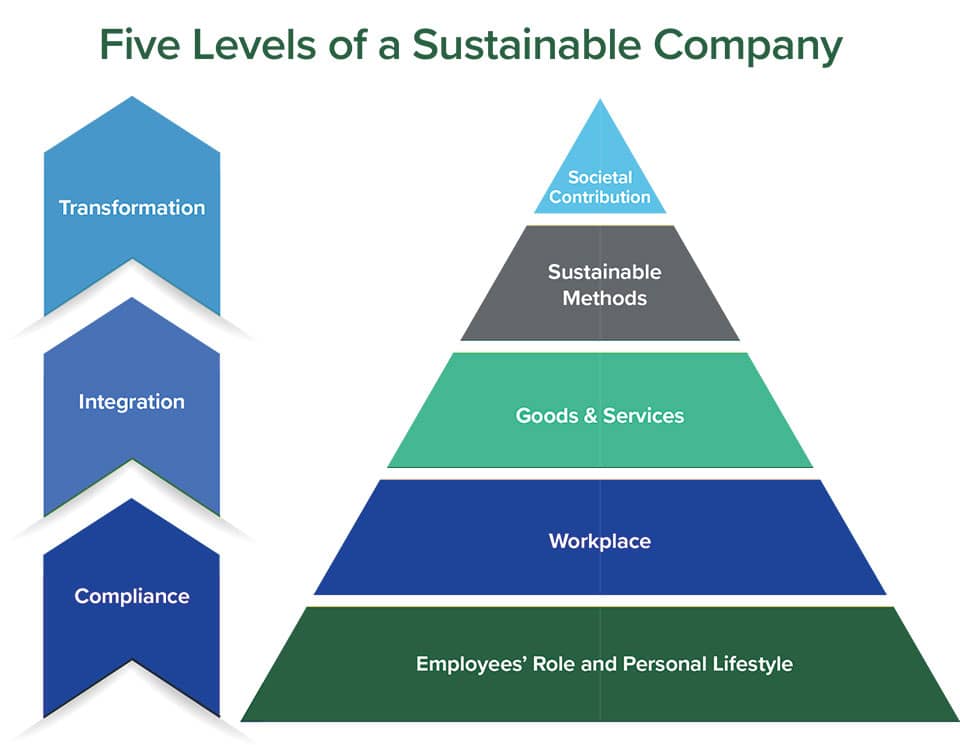
In today's business environment, sustainability has transitioned from a corporate buzzword to a fundamental business imperative. Organizations are increasingly recognizing that their long-term success depends not just on financial performance, but on their ability to operate responsibly within environmental limits. At the heart of this transformation lies Green Human Resource Management (Green HRM)—a powerful strategic approach that integrates environmental sustainability into the core of people management practices.
This article explores how Green HRM serves as a catalyst for organizational sustainability, examining the mechanisms through which it strengthens environmental performance, enhances business resilience, and creates lasting competitive advantages.
Understanding the Green HRM-Sustainability Connection

Green HRM represents the intersection of human resource management and environmental sustainability. It encompasses policies, practices, and systems that encourage environmentally friendly behaviors among employees while simultaneously advancing the organization's sustainability objectives. The relationship between Green HRM and organizational sustainability is both direct and reinforcing—as Green HRM practices strengthen, so does the organization's overall sustainability performance.
- Green recruitment and selection
- Environmental training and development
- Green performance management and appraisal
- Environment-based compensation and rewards
- Employee empowerment and participation in green initiatives
- Green organizational culture development
Eight Ways Green HRM Strengthens Organizational Sustainability
1. Building Environmental Competencies Across the Workforce
Green HRM strengthens sustainability by systematically building environmental knowledge, skills, and attitudes throughout the organization. Through comprehensive green training programs, employees at all levels develop the competencies needed to identify environmental challenges, implement sustainable solutions, and make environmentally conscious decisions in their daily work.
- Awareness Training: Educating employees about environmental issues, organizational impact, and individual responsibilities
- Technical Skills: Providing specific training on energy efficiency, waste reduction, sustainable resource management, and green technologies
- Problem-Solving Capabilities: Developing employees' ability to identify and address environmental challenges creatively
- Leadership Development: Preparing managers to champion sustainability initiatives and guide green transformations
When employees possess environmental competencies, organizations benefit from bottom-up innovation, improved compliance, reduced environmental incidents, and enhanced ability to achieve sustainability targets.
2. Embedding Sustainability in Organizational Culture

Perhaps the most profound way Green HRM strengthens sustainability is by cultivating a green organizational culture—a shared set of environmental values, beliefs, and norms that guide employee behavior and decision-making. This cultural transformation ensures that sustainability becomes intrinsic to "how we do things here" rather than an externally imposed requirement.
- Shared Environmental Values: Common commitment to environmental stewardship across all levels
- Visible Leadership: Executive modeling of green behaviors and consistent prioritization of sustainability
- Green Norms: Established expectations for environmentally responsible behavior in daily operations
- Environmental Identity: Employees' personal identification with the organization's sustainability mission
- Celebration of Success: Recognition and celebration of environmental achievements reinforcing cultural values
A strong green culture creates self-reinforcing sustainability momentum, reduces the need for constant oversight, and ensures that environmental considerations are automatically integrated into business decisions.
3. Driving Measurable Environmental Performance Improvement
Green HRM strengthens organizational sustainability by establishing clear accountability mechanisms that translate environmental aspirations into measurable results. By integrating environmental metrics into performance management systems, organizations ensure that sustainability goals receive the same attention and resources as traditional business objectives.
- Environmental KPIs: Specific, measurable targets for energy use, waste reduction, carbon emissions, and resource consumption
- Individual Accountability: Incorporation of environmental objectives into personal performance goals and evaluations
- Team-Based Metrics: Collective environmental performance measures that encourage collaboration
- Balanced Scorecards: Integration of environmental performance alongside financial, customer, and operational metrics
- Regular Reviews: Consistent monitoring and feedback on environmental performance
Organizations that link performance evaluation to environmental outcomes typically achieve 30-40% greater improvement in sustainability metrics compared to those without such integration.
4. Attracting and Retaining Sustainability-Oriented Talent

Green HRM strengthens sustainability by ensuring the organization attracts, selects, and retains employees who are genuinely committed to environmental values. This alignment between individual and organizational environmental priorities creates a workforce that actively drives sustainability initiatives rather than merely complying with them.
- Environmental Employer Branding: Showcasing sustainability commitments and achievements in recruitment materials
- Values-Based Selection: Assessing candidates' environmental awareness and commitment during hiring processes
- Green Onboarding: Integrating environmental orientation into new employee induction programs
- Sustainability Career Paths: Creating opportunities for employees to develop careers in environmental roles
- Green Benefits: Offering environmental benefits such as carbon offset programs, sustainable commuting incentives, and green investment options
Research indicates that 70% of millennials and Gen Z workers consider a company's environmental practices when making employment decisions, making Green HRM essential for talent competitiveness.
5. Fostering Innovation for Sustainable Solutions

Green HRM strengthens sustainability by creating organizational conditions that encourage environmental innovation. By empowering employees to identify environmental challenges and develop creative solutions, organizations tap into distributed intelligence and generate innovations that might not emerge from top-down directives alone.
- Employee Suggestion Programs: Formal systems for submitting and implementing environmental improvement ideas
- Green Teams: Cross-functional groups dedicated to identifying and solving environmental challenges
- Innovation Time: Allocated time for employees to work on sustainability projects
- Resource Provision: Support and resources for testing and implementing environmental innovations
- Failure Tolerance: Safe environment for experimenting with green initiatives without fear of negative consequences
Organizations with strong Green HRM practices generate 50% more environmental innovations than those without, leading to improved processes, reduced costs, and enhanced environmental performance.
6. Enhancing Resource Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Green HRM strengthens organizational sustainability by mobilizing employees to identify and eliminate resource waste throughout operations. When employees are trained, motivated, and empowered to improve environmental efficiency, organizations achieve significant reductions in energy consumption, material waste, and operational costs.
- Energy Conservation: Employee-driven initiatives reducing electricity, heating, and cooling consumption
- Waste Reduction: Systematic identification and elimination of waste throughout operations
- Water Management: Conservation programs reducing water consumption and improving wastewater treatment
- Material Efficiency: Optimized use of raw materials and supplies
- Circular Economy Practices: Reuse, recycling, and regeneration initiatives extending resource lifecycles
Organizations implementing comprehensive Green HRM typically achieve 15-30% reductions in resource consumption and associated costs within three years, demonstrating that environmental sustainability and financial performance are complementary rather than competing objectives.
7. Strengthening Stakeholder Relationships and Corporate Reputation

Green HRM strengthens organizational sustainability by enhancing relationships with critical stakeholders including customers, investors, regulators, communities, and employees themselves. When organizations demonstrate genuine commitment to environmental responsibility through their HR practices, they build trust, credibility, and social license to operate.
- Customer Loyalty: Environmentally conscious consumers preferring sustainable brands
- Investor Confidence: ESG-focused investors recognizing comprehensive sustainability management
- Regulatory Compliance: Proactive environmental management reducing compliance risks and penalties
- Community Relations: Local communities supporting organizations that demonstrate environmental stewardship
- Employee Pride: Workforce satisfaction from working for environmentally responsible employers
- Media Coverage: Positive recognition of sustainability leadership enhancing brand reputation
Strong environmental reputation, supported by authentic Green HRM practices, translates directly into business value through enhanced brand equity, reduced regulatory scrutiny, and improved access to capital and markets.
8. Building Organizational Resilience for Long-Term Viability

Perhaps most fundamentally, Green HRM strengthens organizational sustainability by building resilience—the capacity to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and adapt to environmental changes and disruptions. Organizations with strong Green HRM are better positioned to navigate the transition to a low-carbon economy and thrive amid increasing environmental uncertainty.
- Climate Adaptation: Workforce prepared to respond to climate-related business disruptions
- Regulatory Preparedness: Proactive compliance capacity anticipating tightening environmental regulations
- Supply Chain Stability: Sustainable practices reducing vulnerability to resource constraints
- Competitive Positioning: Early-mover advantages in sustainable business practices
- Innovation Capacity: Organizational agility to develop new sustainable products and services
- Stakeholder Trust: Social capital providing buffer during challenging transitions
Implementation Framework: Integrating Green HRM for Sustainability

To effectively strengthen organizational sustainability through Green HRM, organizations should follow a systematic implementation approach:
- Conduct environmental audit of current HR practices
- Assess organizational environmental impact and opportunities
- Define clear sustainability objectives aligned with business strategy
- Identify key stakeholders and secure leadership commitment
- Develop comprehensive Green HRM strategy and roadmap
- Integrate environmental criteria into recruitment and selection
- Design and launch environmental training programs
- Establish environmental performance metrics and reporting systems
- Create green teams and employee engagement mechanisms
- Develop environmental recognition and reward programs
- Implement organization-wide sustainability communications
- Embed environmental values into leadership development
- Celebrate and publicize environmental successes
- Strengthen green norms through consistent reinforcement
- Expand employee participation in sustainability initiatives
- Refine practices based on performance data and feedback
- Scale successful pilot programs across the organization
- Develop advanced environmental competencies and certifications
- Foster systematic environmental innovation processes
- Benchmark against leading organizations and international standards
- Regular review and updating of Green HRM practices
- Response to emerging environmental challenges and opportunities
- Integration of new technologies and methodologies
- Expansion of sustainability scope and ambition
- Sharing learnings and best practices internally and externally
Measuring the Impact: Key Performance Indicators
To demonstrate how Green HRM strengthens organizational sustainability, organizations should track both environmental outcomes and HR-specific metrics:
- Carbon emissions reduction (total and per employee)
- Energy consumption efficiency improvements
- Waste reduction and recycling rates
- Water consumption reduction
- Sustainable resource procurement percentage
- Environmental compliance record
- Percentage of employees completing environmental training
- Employee environmental engagement scores
- Number of environmental improvement suggestions submitted
- Environmental innovation implementation rate
- Green performance metrics achievement rates
- Employee environmental behavior change measures
- Cost savings from resource efficiency improvements
- Environmental reputation and brand perception scores
- Talent attraction and retention rates
- Stakeholder satisfaction with environmental performance
- ESG ratings and sustainability recognition
- Market share in green product/service categories
Overcoming Implementation Challenges

While Green HRM offers substantial benefits for organizational sustainability, implementation often encounters challenges:
Challenge 1: Limited Initial Resources
Solution: Start with low-cost, high-impact initiatives such as environmental awareness campaigns, waste reduction programs, and employee engagement activities. Build business case with early wins to secure additional resources.
Challenge 2: Employee Resistance or Skepticism
Solution: Involve employees early in planning and implementation. Demonstrate personal benefits alongside organizational advantages. Provide education addressing environmental concerns and misconceptions.
Challenge 3: Measurement Difficulties
Solution: Establish baseline metrics before implementation. Use both quantitative environmental data and qualitative behavioral assessments. Leverage technology for automated tracking and reporting.
Challenge 4: Competing Business Priorities
Solution: Frame sustainability as strategic imperative rather than discretionary initiative. Demonstrate links between environmental performance and business outcomes. Integrate sustainability into core business processes.
Challenge 5: Knowledge and Skill Gaps
Solution: Invest in comprehensive training and development. Partner with external experts and consultants. Create learning communities and peer knowledge sharing mechanisms.
Challenge 6: Short-Term Pressure vs Long-Term Goals
Solution: Identify quick wins that deliver immediate results. Establish clear milestones demonstrating progress toward long-term objectives. Communicate both short-term achievements and long-term vision.
Case Examples: Green HRM Strengthening Sustainability

Manufacturing Sector: Automotive Industry Leader
A global automotive manufacturer implemented comprehensive Green HRM practices including environmental competency development for all employees, green innovation teams, and sustainability-linked performance bonuses. Within five years, the organization achieved 42% reduction in manufacturing emissions, 35% decrease in water consumption, and 28% improvement in material efficiency. Employee environmental engagement scores increased from 52% to 89%, and the company was recognized as industry sustainability leader.
Service Sector: Hospitality Chain
An international hotel chain integrated Green HRM across its properties worldwide, focusing on employee training in sustainable operations, green guest service protocols, and environmental innovation programs. Results included 31% reduction in energy consumption per guest night, 45% decrease in water usage, 65% waste diversion from landfills, and significantly improved customer satisfaction scores related to environmental responsibility. Employee retention improved by 18%, attributed partly to pride in working for sustainable organization.
Technology Sector: Software Company
A mid-sized software company implemented Green HRM emphasizing remote work policies, carbon-neutral operations, environmental education, and employee-led sustainability projects. Despite rapid growth, the company maintained carbon-neutral status, achieved zero-waste offices, and established reputation as environmental leader in the tech sector. These efforts contributed to 40% improvement in talent attraction metrics and 25% higher employee engagement scores.
The Future of Green HRM and Organizational Sustainability

As environmental challenges intensify and stakeholder expectations evolve, the role of Green HRM in strengthening organizational sustainability will only grow more critical. Several emerging trends will shape this evolution:
- AI-Powered Green HRM: Artificial intelligence enabling personalized environmental behavior change programs, predictive sustainability analytics, and automated environmental impact tracking
- Regenerative Practices: Shift from "doing less harm" to actively restoring environmental systems through workforce practices
- Climate Adaptation Focus: Growing emphasis on building workforce resilience to climate change impacts
- Circular Economy Integration: Green HRM practices specifically designed to support circular business models
- Global Standards and Certifications: Emergence of universal Green HRM frameworks and professional certifications
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Expanding Green HRM beyond organizational boundaries to include supply chain partners and communities
Conclusion: The Strategic Imperative
Green HRM is not simply an environmental initiative—it is a comprehensive strategic approach that fundamentally strengthens organizational sustainability across multiple dimensions. By building environmental competencies, embedding sustainability in culture, driving measurable performance improvement, attracting committed talent, fostering innovation, enhancing efficiency, strengthening stakeholder relationships, and building resilience, Green HRM creates powerful reinforcing cycles that advance both environmental and business objectives.
The evidence is compelling: organizations that effectively implement Green HRM consistently outperform peers on environmental metrics while simultaneously achieving superior business results including cost reduction, enhanced reputation, improved employee engagement, and stronger competitive positioning.
In an era of intensifying environmental challenges and rising stakeholder expectations, organizational sustainability is no longer optional—it is essential for long-term viability and success. Green HRM provides the strategic framework and practical mechanisms to make sustainability real, measurable, and embedded in daily operations through the most powerful organizational resource: people.
The question for organizational leaders is not whether to implement Green HRM, but how quickly and comprehensively they can mobilize their workforce to strengthen sustainability and secure their organization's future in a rapidly changing world. The time to act is now—and Green HRM provides the roadmap for the journey ahead.
References
- Dumont, J., Shen, J., & Deng, X. (2017). Effects of green HRM practices on employee workplace green behavior: The role of psychological green climate. Human Resource Management, 56(4), 613–627. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21876
- Jackson, S. E., Renwick, D. W., Jabbour, C. J., & Muller-Camen, M. (2011). State-of-the-art and future directions for green human resource management. German Journal of Human Resource Management, 25(2), 99–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/239700221102500201
- Jabbour, C. J. C., & Santos, F. C. A. (2008). The central role of human resource management in the search for sustainable organizations. International Journal of Human Resource Management, 19(12), 2133–2154. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585190802479389
- Kim, Y. J., Kim, W. G., Choi, H.-M., & Phetvaroon, K. (2019). The effect of green human resource management on hotel employees' eco-friendly behavior and environmental performance. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 76, 83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.04.014
- Pham, N. T., Hoang, H. T., & Nguyen, L. D. (2020). Green human resource management and employee green behavior: The role of green rewards. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(4), 1765–1777. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2421
- Renwick, D. W., Redman, T., & Maguire, S. (2013). Green human resource management: A review and research agenda. International Journal of Management Reviews, 15(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12000
- Tang, G., Chen, Y., Jiang, Y., Paillé, P., & Jia, J. (2018). Green human resource management practices: Scale development and validity. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources, 56(1), 31–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7941.12128
- Green Training Associates. (2023). Five levels of a sustainable company. Image. Retrieved from https://greentrainingassociates.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Five-Levels-of-a-Sustainable-Company_03.jpg
- Strategic Connections. (2022). SCI logo. Image. Retrieved from https://www.strategicconnections.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/SCI-Logo-e1661293306206.png
- Chartexpo. (2025). Performance metrics illustration. Image. Retrieved from https://chartexpo.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/performance-metrics.jpg
- Aditya Kulkarni. (2024). Stakeholder relations. Image. Retrieved from https://adityakulkarni.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/img_2771.jpg
- The Helix Foundation. (2024). Classic word cloud H/W layout. Image. Retrieved from https://thehelixfoundation.ca/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Classic-Word-Cloud-H_W-layout.jpeg
- YouTube. (n.d.). How Green HRM strengthens organizational sustainability. Video. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r2XE87EoI7M
- YouTube. (n.d.). Embedding sustainability in organizational culture. Video. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6uLN9dVfOBI
- YouTube. (n.d.). Fostering innovation for sustainable solutions. Video. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GG-IBbfQFY8
Fantastic insights! This article clearly shows that Green HRM is more than an environmental initiative, it’s a strategic driver of organizational sustainability and business success. By embedding sustainability into culture, performance, and talent management, organizations can achieve measurable environmental impact while boosting engagement, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
ReplyDeleteThank you - Happy to hear your perspective.
DeleteThe post makes a good case for why Green Human Resource Management (Green HRM) matters highlighting how HR practices can support sustainability goals and benefit both organizations and the environment. However, it remains mostly theoretical and doesn’t show many real-world examples or evidence of successful implementation. Without concrete cases or practical insights, the argument stays informative but feels more aspirational than convincing.
ReplyDeleteManny thanks for your valuable remarks.
DeleteNice post! Your points are clear and very relevant, especially the way you explain balancing modern HR practices with human-centered management. It’s a thoughtful perspective that really highlights the importance of people in the workplace.
ReplyDeleteThank you for your positive feedback.
DeleteNice post! I found your take on Green HRM really easy to understand. It’s great to see how sustainability and caring for the environment can go hand in hand with smart, people-centered HR practices. Thanks for sharing full idea.
ReplyDeleteAppreciate your time and feedback, Gayangi !!
DeleteI truly value the way you explained the connection between HR strategy and environmental responsibility it brings clarity to a complex topic.
ReplyDelete